SAP FICO (Financial Accounting & Controlling)
SAP FICO is one of the most popularly used SAP modules. This is used by companies for handling their financial data. It is a combination of two modules – SAP FI and SAP CO. As business operations are executed daily, a lot of financial data is generated. This includes sales orders, transactions, and purchases. The software is also used along with SAP ECC.
.jpg)
In this post, we will talk about the different features of SAP FICO, its functions, advantages, and implementation.
What is SAP FICO?
SAP FICO consists of two modules - SAP Finance (FI) and SAP Controlling (CO). Both of these modules are designed for specific functions. The SAP FI module deals with financial accounting and reporting. The CO module deals with monitoring costs and financial planning. The software aims to assist companies to make the process of financial planning and analysis easier. All this helps in making better financial decisions.
SAP FICO can be integrated with other SAP Logistics modules, including –
- Sales and Distribution (SD)
- Quality Management (QM)
- Production Planning (PP)
- Materials Management (MM)
- Plant Maintenance (PM)
SAP FI (Finance)
SAP FI can integrate different modules into a single system for the company. This software offers all the features for handling financial transactions and accounts. The reports generated by SAP FICO are used widely by banks, tax authorities, managers, and stakeholders. The software also generates financial statements. These include profit/loss statements and balance sheets.
SAP FI has the following sub-modules that have specific functionalities –
i) General Ledger –This is used to provide a complete report for internal/ external accounting. It contains the company’s transaction data and lists all the accounts. These can be recorded in sub-modules in real-time.
ii) Accounts Receivable –These are records that are used to manage all customer accounting data. It is also used to manage customer accounts and transactions. These transactions include invoice payments, down payments, invoice posting, and customer reports.
iii) Accounts Payable –These records have vendor accounting data. It also consists of data regarding vendor transactions and vendor accounts.
iv) Asset Accounting –This sub-module is used for managing the company’s assets. This includes all fixed assets such as heavy equipment, land, and buildings. The module also has asset transactions including sales, transfers, revaluations, and asset acquisitions.
v) Bank Ledger –This contains all the bank account transaction data. It can merge all transaction data on bank statements. Then, it can compare the data with transactions stored in the system.
vi) Consolidation –This sub-module allows the company to combine all financial statements from multiple entities. It also provides a complete view of the firm’s financial health.
vii) Funds Management– It is used for managing the budgets for revenues and expenses.
Special Purpose Ledger– This defines the SAP FI ledgers for financial reporting.
Travel Management– This manages all transactions regarding travel processes. This will include booking trips and managing travel expenses.
Implementation of SAP FI
To implement SAP FI, it needs to be configured. The Business Manager has to make the primary configurations. These configurations are required to gather client needs, business requirements, and other configurations. After this, all financial statements and Master Data is migrated to SAP FI. This configuration process also requires currencies, fiscal year variants, and charts of accounts.
After the process is over, document posting is posted automatically. This allows companies to observe their financial status in real-time. This, in turn, enables the company to track all their financial transactions, which also helps in financial reporting at the end of their financial year.
SAP CO (Controlling)
This module supports monitoring, controlling, and optimization of business processes. It includes facilities for managing master data. This data covers cost centres, internal orders, cost elements, and other areas. The main purpose of introducing this module is planning. Companies can compare their planned data and actual business data to analyze the variances.
The different sub-modules of SAP CO are given below along with their functionalities –
i) Cost Elements –This provides you with an overview of the costs and revenues of the company. These are based on income statements. Cost element accounting defines the cost origins and also represents different company costs. Most of these values are transferred from Financial Accounting to Controlling.
ii) Cost Centers Accounting –This sub-module is used for controlling activities. It deals with the expenses associated with the company’s internal departments. These departments include marketing, production, sales, and HR. The Cost Center includes only expenses and not revenues.
iii) Profit Centers –It consists of all the cost data about the company’s business lines. This module deals with expenses and revenues.
iv) Internal Orders –The module is used for managing all expenses of smaller internal projects/ non-fixed assets.
v) Profitability Analysis –Companies analyze their profit and losses using this sub-module. This is a vital process for decision-making. Measuring product profitability, pricing, and evaluating target markets. This eases the process of profitability analysis for each region of business. Additionally, customer profitability, distribution channels, and product types can also be analyzed.
vi) Product Costing –This module deals with all the costs related to the company’s goods and services. This helps in optimizing business efficiency and manufacturing costs.
Implementation of SAP CO
The implementation of SAP CO is essential for any company to analyze cost data of internal management processes. SAP CO implementation helps companies to handle the database of business information. A proper implementation will lead to business reporting and decision making.
Benefits of SAP FICO
The most useful benefits of using SAP FICO are –
- It generates all the accounting data of a business in one place for managing finances
- Other SAP modules such as Material management and Production planning can be integrated with this SAP FICO for making important decisions
- All transactions generated in the logistics department can be posted in real-time to the Financial Accounting modules. This helps in handling accounts better and storing these transactions properly
- The SAP FI module can be used to effectively automate credit management and collections
- SAP FI enhances the accounts payable and accounts receivable functions by offering easy invoice payments
- Companies can handle their company’s cash across countries using SAP FI
- With SAP CO, planning, monitoring, and reporting costs is easier
- SAP CO offers procedures for analyzing and observing overheads required for financial reporting
- The SAP FICO software assists companies in improving financial operations
SAP FICO Certification & Career Scope
Having a solid background in SAP FICO helps employees to handle reporting and finance accounting better. It is important to learn about the business environment, financial planning, and asset accounting. There are several training paths which you can choose –
- SAP S/4HANA Financial Accounting
- SAP ERP Management Accounting
- SAP S/4HANA Management Accounting
- SAP ERP Financial Accounting
- Treasury Management
- Cash Management
Some institutes also offer a comprehensive SAP FICO course. This usually lasts for 6 months.
An individual having comprehensive knowledge about SAP FICO and its sub-modules can get employed as a SAP FICO Consultant. Having 2 to 3 years of experience in working with SAP FICO modules will help them become a successful SAP FICO consultant.
Read Here: SAP FICO Training
Educational Background
To become a successful employee in the FICO field, he/ she needs to have an educational background in Finance, Accounting, and Management. A UG degree in any of these subjects will be great for candidates to understand the SAP FICO courses better. Additional courses in Accounting and Financial Management will be a plus.
Skills required to be a SAP FICO Consultant –
- Experience in financial accounting, professional services, distribution, management accounting, and Fixed Asset Accounting
- A thorough understanding of accounting business processes
- At least 5 years of experience in financial support projects
Salary Structure
The primary role of a SAP FICO Consultant is to implement the SAP FICO module for his/her company. They refine existing financial methods and perform system configuration. All this is based on the particular business needs and financial condition. The consultant must also have the ability to understand the client’s point of view.
On average, a SAP FICO Consultant earns INR 6,87,233 annually. The salary starts at 359 LPA. With a few years of experience and skills in finance and accounting, the candidate can rise in the ranks of the finance department with a SAP FICO certification under his belt.
Major companies hiring SAP FICO Consultants –
- Accenture
- IBM
- Cognizant Technology Solutions
- Tata Consultancy Services
- NTT DATA
- Tech Mahindra
- Capgemini
Conclusion
The SAP FICO software set has been proven to be the foundation of finance and controlling for modern organizations. It has successfully enhanced the financial operations of many companies. Thus, many more companies are adopting it. And career-wise, it is great for employees in finance or human resource looking to take their career to the next level.
Tutorials
- Accounting Entries
1.1 All the Inventory transactions will look for the valuation class and the corresponding G.L. Accounts and post the values in the G.L accounts.For Example: During Goods ReceiptStock Account & ...  General setting for SAP system, Date Time, Currency and Number format
General setting for SAP system, Date Time, Currency and Number format
General setting for your SAP system, Date Time, Currency and Number format You can do the general setting for currency, date time, number format Through T-Code SU01 in general setting tab SPR ... SAP FICO Career, Scope and become Certified Consultant
SAP FICO Career, Scope and become Certified Consultant
Scope and Opportunity of a Career in SAP FICO In depth knowledge of essential ERP Systems is a must for those wanting to get their hands on the implementation of the entire SAP Life Cycle and get e ... SAP FICO Training Material with Screen Shots
SAP FICO Training Material with Screen Shots
This tutorial contains the Complete list of SAP FICO Training Material with Screen Shorts Create a Company Code (OX02) T-code (OX02) Path Enterprise Structure Definition Fina ... SAP FI (Financial Accounting) Module
SAP FI (Financial Accounting) Module
SAP FI (Financial Accounting) IntroductionThe SAP FI CO (Financial Accounting & Controlling) Module has the capability of meeting all the accounting and financial needs of an organization. It is w ... SAP FICO Certification Fee and Course Duration in India
SAP FICO Certification Fee and Course Duration in India
The SAP FI/CO course begins with a business analysis by defining business environment, procedures and planning methodologies. Then financial accounting, asset accounting is understood and la ... ASSET ACCOUNTING Configuration Steps
ASSET ACCOUNTING Configuration Steps
How to Configure ASSET ACCOUNTING in SAP FICO?Step 1 – COPY CHART DEPRECIATIONEC08 – IMG>Financial Accounting > Asset Accounting > FI-AA Implementation Guide (Simplified Version) ... Withholding Tax in SAP
Withholding Tax in SAP
Detail information about Withholding Tax1. Types of withholding Tax a. Standard Withholding Tax provides the following features:i. Withholding tax for accounts payableii. Withholding tax calculat ... Create New Tax code in SAP
Create New Tax code in SAP
T.code FTXP is used to create Tax code.All the Taxes are divided into two categories. Input tax: All taxes related to purchase are considered as Input tax. Output tax: All taxes on sales come under th ... Indian Tax Procedure Migration from TAXINJ to TAXINN.
Indian Tax Procedure Migration from TAXINJ to TAXINN.
Tax Migration as a prequisition to legal change GST.1. The TAXINJ tax procedure is currently in use. What are the prerequisite changes that need to be done for GST?Ans: For GST regime solution adoptio ... Configure SAP Cash Journal
Configure SAP Cash Journal
In the SAP SAP tutorial, we will learn the step-by-step procedures to configure SAP Cash Journal with proper screenshots of every configuration step. What is SAP Cash Journal? The SAP ...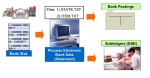 Configure the Electronic Bank and Manual Bank Statement
Configure the Electronic Bank and Manual Bank Statement
Electronic bank statement – It is an electronic document sent by the bank which gives details of the transactions done by the account holder. The electronic document can be remitted by the bank ... Transactions FBL1N/ FBL3N/ FBL5N or as of ERP2004 FAGLL03: Defining Special Fields
Transactions FBL1N/ FBL3N/ FBL5N or as of ERP2004 FAGLL03: Defining Special Fields
How to define Special Fields for the Line Item Transactions FBL1N/ FBL3N/ FBL5N or as of ERP2004 FAGLL03?I. Basic information1. Depending on your release, you can define the special fields for the lin ... TAX and Pricing Procedure Configuration for GST
TAX and Pricing Procedure Configuration for GST
Tax Procedure Configuration for GST 1) Create Condition Table These condition table combinations are for user reference with the help of these and you create your own condition table as per your ....jpg) Configuration of Foreign Exchange
Configuration of Foreign Exchange
Foreign Currency Valuation Configuration Step-I: Define standard quotation for exchange rate Path: General Setting> Currencies> Define Standard quotation for exchange rate Click o ... Define Document Number Range
Define Document Number Range
T-code(FBN1)PathFinancial Accounting -> Financial Accounting Global Setting -> Documents -> Document Number Ranges -> Define/Copy (co code or Fiscal Year)In this activity, you create numbe ... Asset Accounting (FI/AA) Create view
Asset Accounting (FI/AA) Create view
Organizational Structure:Check- Country Specific SettingsMaximum LVA amount for posting: Here we define the maximum amount for checking posting to low-value assets.Net book value for changeover of dep ... SAP FICO Tree Menu
SAP FICO Tree Menu
Sap tree_ficoSAP standard menu||-- Office|-- Logistics|-- Accounting| || |-- Financial accounting| | || | |-- General ledger| | | || | | |-- Document entry| | | | || | | | |-----G/L account posting F- ... Leading ledger vs Non-leading ledger in ECC 6.0
Leading ledger vs Non-leading ledger in ECC 6.0
Difference between Leading ledger and Non- leading ledger New General Ledger has all functions of the Classic General Ledger but has been enhanced with special ledger functions to create greater ... Define Document Types
Define Document Types
What is Document Types in SAP? Document type is a key used for classifying accounting documents & differentiate between trade transactions to be posted. SAP users enter the document type in the ...